


月球角砾岩NWA 7948岩屑特征及其对月壳组成的启示
About 381 kg of lunar samples have been returned from the equatorial latitudes of lunar nearside by six Apollo missions and three Luna missions. However, these sampling sites were restricted to a smaller areas representing only ~4.4% of the surface of the Moon. The lunar meteorites, which were ejected from random locations across the lunar surface, are thought to can provided valuable information to extend our knowledge of the composition and geological evolution history of the Moon. To date, over 320 individual (named) lunar meteorites have been recovered from hot and cold deserts around the world including Oman, Northwest Africa, and Antarctica (Meteoritical Bulletin Database). The widespread sampling represented by these meteorites are an important supplement to the Apollo and Luna returned rocks.
Northwest Africa (NWA) 7948, weighing 59.8 g, was recovered in 2013 (Meteoritical Bulletin Database). We acquired one slice of NWA 7948 from Eric Twelker who hold the main mass of this meteorite. In a polished thick section (~3.6 cm2), a wide variety of crustal lithologies from mare basalts (rocks that were made in ancient volcanic eruptions), highland regions, as well as surficial regolith components (volcanic glass and impact glass) are present; making this meteorite a good target for understanding the composition and lithological variability of the lunar crust. In addition, we also discovered a compositionally unusual metal-rich clast. It exhibits metal-rich texture, non-lunar-like chemical element trends, and unusual mineral chemistry. Our studies suggest that this unusual lithic clast is not similar to the meteorites sourced from other bodies (e.g., Vesta and Mars) in the Solar System, but most likely represents an impact lithology generated by melting of a magmatic rock type (called the Mg-suite) on the Moon.
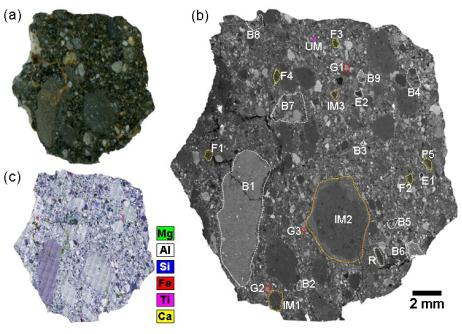
Scanned sample surface image (a), SEM image showing labelled rock fragment names (b), and false-color X-ray element map (c) of lunar meteorite NWA 7948.
The geochemical composition and shock feature of NWA 7948 were investigated by a range of analytical lab techinques including Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) and Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrometer. Petrologic, geochemical, and remote sensing data suggest that the NWA 7948 meteorite is compositionally most similar to regions on the nearside highlands-mare boundaries (e.g., Mare Crisium) or a cryptomare region (e.g., Schickard-Schiller) or a farside highlands-mare boundaries (e.g., Apollo basin in the South Pole–Aitken region). Our studies shown that NWA 7948 may represent lunar material that has not been reported before. The multiple lithic clasts and the compositionally unusual clasts within NWA 7948 reveal that the launch site of NWA 7948 has a complex geological diversity, and also suggest that there is much to learn about the Moon’s petrological makeup.
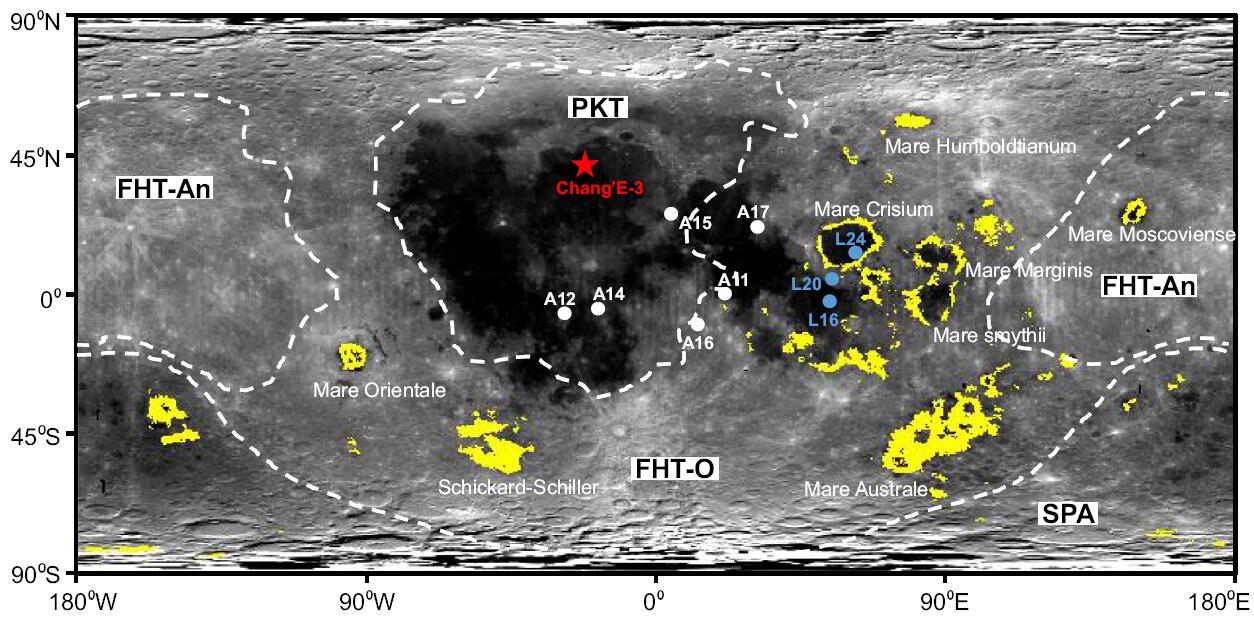
Image showing that the areas where surface regolith FeO and Th contents obtained by the Lunar Prospector Gamma Ray Spectrometer match the chemcial composition of lunar meteorite NWA 7948 in yellow. These yellow regions may represent the source site of the meteorite. The Apollo landing sites(A), Luna landing sites (L) and Chang’E 3 landing site are shown for context along with the made geochemical terranes (PKT, FHT, SPA). Image: adapted from Zeng et al. 2018a (MAPS)
____________________________________________
Full citation: Zeng, X., Joy, K. H., Li, S., Pernet‐Fisher, J. F., Li, X., Martin, D. J., Li, Y. & Wang, S. (2018). Multiple lithic clasts in lunar breccia Northwest Africa 7948 and implication for the lithologic components of lunar crust. Meteoritics & Planetary Science. doi: 10.1111/maps.13049
Download attachments: